
Reusing older batteries with newer one, or installing batteries of mixed capacities into a device, also makes them more prone to leakage. The flow of excess current in a short-circuited battery causes its temperature to rise, making it significantly more susceptible to leakage. Where this is not possible, batteries should be individually wrapped in plastic. Batteries are best stored in their original packaging. Contact with other batteries or metallic items that can substantially increase the risk of short circuiting. Tossing your batteries into a bin containing paper clips or other metallic items for later reuse, or into a purse or pocket containing keys or coins is strongly discouraged. Whether being transported or stored, batteries should never come into contact with metallic items or other batteries. Conversely, high temperatures accelerate the rate of self-discharge.Ĭontact with other items. (The 32☏/0☌ freezing point applies to water, not chemical compounds.) In fact, batteries should never be permitted to freeze, and refrigeration is neither required nor recommended by battery manufacturers. The clearly freezing temperature at the lower extreme of -40☏/C will not freeze certain battery chemistries, for example, lead acid but such an extremity can negatively affect its chemical composition. The range at polar extremes allows for –40☏ to 122☏ (–40☌ to 50☌).

Storage recommendation for most batteries is in an ambient temperature of around 59☏ (15☌) and low humidity. Another factor that is widely shared is battery contact with other materials. Shelf life is the length of time your disposable battery will retain its charge unused, or in the case of rechargeable batteries, how long before it will require a charge or is considered spent.Īpart from capacity during storage, the ideal, ambient storage temperatures is the same for battery chemistries across the board with some nuances at the extreme ranges. Where self-discharge focusses on rate of speed, shelf life is concerned with duration. This term is closely connected with self-discharge. All batteries self-discharge over time even when idle.īattery shelf life. Self-discharge denotes the rate at which the battery self-depletes in idle storage. Discharge occurs at variable rates based on chemistry, brand, storage environment, temperature. As soon as a battery is manufactured, it immediately begins to lose its charge-it discharges its energy. Most recognized manufacturers set it off from surrounding text with distinguishing features such as boxing, color, or separation.īattery self-discharge rate.
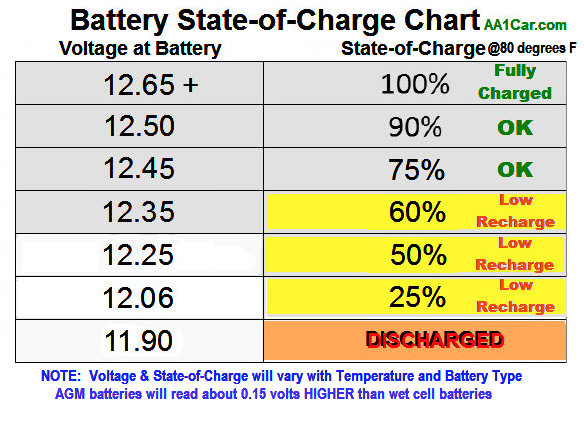
You can find your battery’s expected date of expiration on the packaging or the battery. As a rule of thumb, when your battery’s total self-discharge is over 20 percent, you can consider the battery expired.
D BATTERY VOLTAGE CHART FULL
An expired battery denotes the inability of its manufacturer to guarantee its full charge upon a certain date. Expiration as applied to energy storage devices does not mean the same as its application to food items. We will also take a look at the effects of capacity loss and regulations for shipping and travel.įirst, it is important to clarify the meaning of key terms:īattery expiration. In this post we will discuss the storage of nickel-based (i.e., Ni-MH and Ni-CD), lithium, alkaline, and lead acid batteries. While all batteries share similarities in the storage process, key differences and nuances exist that are chemistry specific.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
